Measuring HR’s actions and their influence on commercial outcomes involves assessing both qualitative and quantitative factors. HR’s effectiveness can directly impact areas such as employee engagement, productivity, retention, and ultimately, profitability. Here’s a structured approach to measure HR’s influence on commercial outcomes:
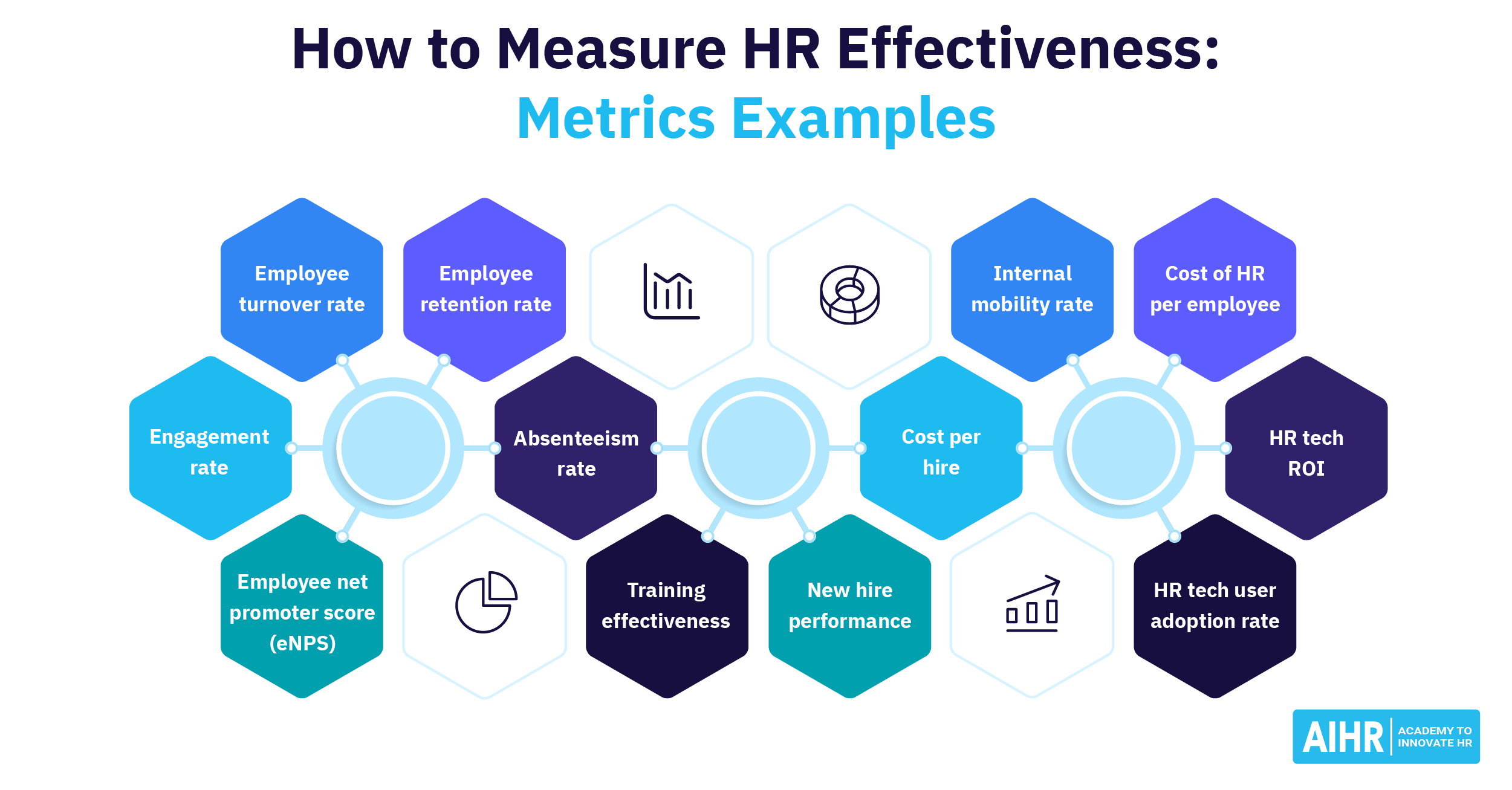
1. Key Metrics to Measure HR’s Performance:
- Employee Retention Rate: High turnover can indicate issues with hiring, training, or employee satisfaction. Reducing turnover saves costs on hiring and training.
- Employee Engagement Scores: Engaged employees tend to be more productive and aligned with business goals, contributing to better commercial outcomes.
- Time-to-Fill and Time-to-Productivity: How quickly HR can recruit and onboard new employees, and how soon they start contributing value.
- Training and Development ROI: Tracking the return on investment for learning programs through employee performance improvements or skill enhancements.
- Absenteeism Rate: High levels of absenteeism can reduce productivity, influencing revenue and customer satisfaction.
2. Commercial Outcomes Linked to HR Actions:
- Revenue per Employee: This measures how efficiently HR selects and manages talent. Higher productivity leads to more revenue generation.
- Customer Satisfaction and Retention: Happy and motivated employees (especially in customer-facing roles) tend to offer better service, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Innovation and Time-to-Market: HR’s investment in skills and talent development can drive innovation, leading to faster product launches or service enhancements.
- Operational Efficiency: Through workforce planning and performance management, HR can optimize how the business operates, reducing costs and improving profit margins.
- Cost Per Hire: By reducing recruitment costs and hiring the right talent faster, HR can directly impact operational savings.
3. Ways HR Actions Impact Commercial Outcomes:
- Employee Experience & Engagement: When HR fosters a positive work culture, it increases job satisfaction and retention. This directly leads to more consistent performance and reduced costs associated with high turnover.
- Performance Management: HR’s role in setting KPIs, providing feedback, and ensuring employees are aligned with the company’s goals results in improved individual performance, which translates into better team output and commercial success.
- Learning and Development: Effective training programs ensure employees have the skills to meet evolving business needs. HR’s investment in professional development can increase productivity, innovation, and competitive advantage.
- Diversity & Inclusion Initiatives: Diverse teams often perform better by bringing a range of perspectives and ideas, which can improve problem-solving and customer outcomes.
4. Linking HR Metrics to Commercial KPIs:
- Engagement and Productivity → Sales Performance: Higher engagement often leads to higher productivity, which translates into better sales performance and customer service.
- Retention Rate → Reduced Costs: Lower turnover decreases the need for frequent hiring and training, reducing HR expenses, which impacts the bottom line.
- Employee Training → Customer Satisfaction: Well-trained employees tend to provide better service, leading to higher customer satisfaction and potentially higher lifetime value (LTV) for customers.
5. HR as a Strategic Business Partner:
HR influences commercial outcomes when aligned with business goals. For example:
- Strategic Workforce Planning: HR can anticipate future skill needs, ensuring the right talent is in place to meet commercial objectives.
- Cultural Alignment: HR fosters a company culture that supports innovation, collaboration, and customer-centricity, all of which enhance the company’s market position.